OmegaPure
 At the same time as the media increases consumer awareness of the importance of fish oils, manufacturers face the challenge of eliminating heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). The industry-leading technologies used in the preparation of the fish oils surpass the standards for environmental pollutants, including dioxins, PCBs, pesticides, and heavy metals such as mercury.
At the same time as the media increases consumer awareness of the importance of fish oils, manufacturers face the challenge of eliminating heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). The industry-leading technologies used in the preparation of the fish oils surpass the standards for environmental pollutants, including dioxins, PCBs, pesticides, and heavy metals such as mercury.
OmegaPure oils are processed through special molecular distillation. Molecular distillation is commonly used to purify and concentrate fish oils. In this process, the fish oil is broken down into its basic molecular components and separated by molecular weight. Due to varying molecular weights, specific components can be removed from or concentrated in the oil. This ensures that contaminants can be reduced to levels far below industry standards. It also allows the manufacturer to increase the concentration of active ingredients. For example, an 18:12 oil can be concentrated through molecular distillation to produce a 30:20 product, as in the case of OmegaPure 600.
Processing a fish oil formula begins with rigorous care and control of the starting raw materials (non-GMO sardines, mackerel, anchovies) to assure optimum oil quality. The oils are distilled in a controlled, pristine vacuum environment to minimize distillation temperatures. The exposure time, even to these lower distillation temperatures, is tightly controlled and uniform, resulting in levels of impurities well below the industry standards. The technology employed for OmegaPure 600 meets special molecular distillation standards. As this oil is a concentrated source of omega-3 fatty acids, our manufacturer goes above and beyond the traditional purification methods to ensure its safety. This is accomplished by:
» A triple-phase molecular distillation purification process to maximize purity while concentrating the EPA and DHA polyunsaturated fatty acids
» Ensuring consistency in contaminant removal, and therefore purity levels, through uniform processing times » Reducing the evaporation stage to half the time of traditional systems to drive down the oxidative risk
The proprietary technologies used in the manufacture of OmegaPure oils are in accordance with pharmaceutical standards that assure safe, consistent fish oils. Furthermore, Revolution Health & Wellness requires regular third-party testing to verify that OmegaPure oils meet the stringent standards we use for freshness, quality, and purity.[1]
Despite aggressive marketing claims to the contrary, a recent publication by Oelrich et al reported that, of the three formulations tested, there was no significant difference in the effect on triglycerides.[2] The active therapy of the three fish oil supplementation arms was 4 g/day of combined EPA and DHA provided as: a) 90% triglyceride (TG) formulation (TG90), b) 60% TG formulation (TG60), or c) ethyl esters (EE) (i.e., 0% TG). Furthermore, omega-3 fish oils provided in an ethyl ester formulation tended to have a lower impact on increasing LDL-cholesterol levels compared to omega-3 fish oils delivered in the triglyceride formulation.*
Research suggests it takes 2 g/day of DHA supplementation for a month to saturate the plasma and three to six months of supplementation to saturate the tissues.[3] Concentrations increase in breast milk within less than a week of DHA supplementation. [3]
Research and studies provide evidence that omega-3 fatty acids antagonize arachidonic acid-induced proinflammatory prostaglandin formation, provide resolvins and protectins to aid the body’s “cleanup” response to the inflammatory cascade, promote neurological health and mental functioning, support a balanced immune response, and support healthy glucose and insulin metabolism.[4-13] Furthermore, supportive but not conclusive research shows that consumption of EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease.*[13-16]
Directions
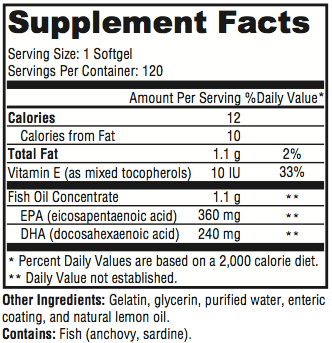
Take 1-2 capsules one to three times daily. We generally guide the dosing recommendations based on lab evaluation of your Omega-3 Index.
References
- Assays available upon request.
- Oelrich B, Dewell A, Gardner CD. Effect of fish oil supplementation on serum triglycerides, LDL cholesterol and LDL subfractions in hypertriglyceridemic adults. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2011 Sep 15. Epub ahead of print. [PMID: 21924882]
- Arterburn LM, Hall EB, Oken H. Distribution, interconversion, and dose response of n-3 fatty acids in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Jun;83(6 Suppl):1467S- 1476S. Review. [PMID: 16841856]
- Storey A, McArdle F, Friedmann PS, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid reduce UVB- and TNF alpha-induced IL-8 secretion in keratinocytes and UVB-induced IL-8 in fibrolasts. J Invest Dermatol. 2005 Jan;124(1):248-55. [PMID: 15654981]
- Kim YJ, Kim HJ, No JK, et al. Anti-inflammatory action of dietary fish oil and calorie restriction. Life Sci. 2006 Apr 18;78(21): 2523-32. [PMID: 16438990]
- Maroon JC, Bost JW. Omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil) as an anti-inflammatory: an alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for discogenic pain. Surg Neurol. 2006 Apr;65(4):326-31. [PMID: 16531187]
- Weylandt KH, Chiu CY, Gomolka B, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids and their lipid mediators: Towards an understanding of resolvin and protectin formation. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2012 Mar;97(3-4):73-82. [PMID: 22326554]
- Kremmyda LS, Tvrzicka E, Stankova B, et al. Fatty acids as biocompounds: their role in human metabolism, health and disease: a review. part 2: fatty acid physiological roles and applications in human health and disease. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2011 Sep;155(3):195-218. doi: 10.5507/bp.2011.052. [PMID: 22286806]
- Frangou S, Lewis M, McCrone P. Efficacy of ethyl-eicosapentaenoic acid in bipolar depression: randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Br J Psychiatry. 2006 Jan;188:46-50. [PMID: 16388069]
- Kankaanpaa P, Sutas Y, Salminen S, et al. Dietary fatty acids and allergy. Ann Med. 1999 Aug;31(4):282-87. [PMID: 10480759]
- Ebbesson SO, Risica PM, Ebbesson LO, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids improve glucose tolerance and components of the metabolic syndrome in Alaskan Eskimos: the Alaska Siberia project. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2005 Sep:64(4):396-408. [PMID:16277123]
- Nettleton JA, Katz R. n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in type 2 diabetes: a review. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005 Mar;105(3):428-40. [PMID:15746832]
- Weitz D, Weintraub H, Fisher E, et al. Fish oil for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cardiol Rev. 2010 Sep-Oct;18(5):258-63. [PMID: 20699674]
- Psota TL, Gebauer SK, Kris-Etherton P. Dietary omega-3 fatty acid intake and cardiovascular risk. Am J Cardiol. 2006 Aug 21;98(4A):3i-18i. [PMID: 16919512]
- Sasaki J, Yokoyama M, Matsuzaki M, et al. Relationship between coronary artery disease and non-HDL-C, and effect of highly purified EPA on the risk of coronary artery disease in hypercholesterolemic patients treated with statins: sub-analysis of the Japan EPA Lipid Intervention Study (JELIS). J Atheroscler Thromb. 2012;19(2):194-204. [PMID: 22186099]
- Zhang J, Wang C, Li L, et al. Inclusion of Atlantic salmon in the Chinese diet reduces cardiovascular disease risk markers in dyslipidemic adult men. Nutr Res. 2010 Jul;30(7):447-54. [PMID: 20797476]