CinnDromeX

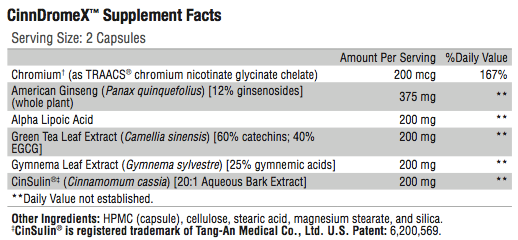
American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) possesses sulfonylurea- like activity. This herb does not lower blood sugar unless it contains a significant quantity of ginsenosides. The American ginseng in CinnDromeXTM is a standardized 12% (ginsenosides) extract.*
Gymnema Leaf Extract (Gymnema sylvestre) is a water-soluble extract made from the leaves of Gymnema sylvestre and standardized to 25% gymnemic acid. This form does not decrease iron absorption as other forms may. Gymnema can enhance the effects of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents by reducing glucose absorption in
the intestine, stimulating pancreatic beta cell growth and possibly increasing endogenous insulin secretion. Gymnema may also reduce serum lipids.*
Green Tea Polyphenols (Camelia sinesis) protect erythrocytes from oxidative stress, possibly reducing risk of late complications of diabetes. In research studies EGCG enhanced insulin activity, protected the pancreatic cells by reducing inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-1beta), and reduced IFN-gamma-induced nitric oxide production. It affected genes that inhibit activation of NF- kappaB and reduced the level of messenger RNA for the hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes.*
Alpha Lipoic Acid is a potent antioxidant that acts by multiple mechanisms, both physiologically and pharmacologically, in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and hypertension.
In higher doses, alpha lipoic acid supports insulin regulation of blood sugar levels.*
Chromium: The Albion® patented process that combines chromium with glycinate and niacin increases its bioavailability and improves insulin sensitivity. Individuals with Type 2 diabetes tend to have lower blood chromium levels. Chromium enhances the metabolic action of insulin and may reduce some of the risk factors for cardiovascular disease, especially in overweight individuals.*
Directions:
Take two capsules twice daily or as directed by your healthcare practitioner.
References:
- Anderson RA, et. al. Isolation and characterization of polyphenol type-A polymers from cinnamon with insulin-like biological activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2004 Jan 14;52(1):65-70. [PMID:14709014]
- Imparl-Radosevich J, et.al. Regulation of PTP-1 and insulin receptor kinase by fractions from cinnamon: implications for cinnamon regulation of insulin signaling. Horm Res. 1998 Sep; 50(3):177-82 [PMID: 9762007]
- Anderson RA, et al. Isolation and characterization of polyphenol type-A polymers from cinnamon with insulin-like biological activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2004 Jan 14:52(1):65-70. [PMID: 14709014]
- Khan A, Safder M, Ali Khan MM, Khattak KN, Anderson RA. Cinnamon improves glucose and lipids of people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003 Dec; 26(12):3215-8. [PMID: 14633804]
- Rotshtyen Y, Zito SW, Application of modified in vitro screening procedure for identifying herbals possessing sulfonylurea-like activity. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004 Aug;93 (2-3):337-44 [PMID: 15234774]
- Sievenpiper JL, Arnason JT, Leiter LA, Vuksan V. Variable effects of American Ginseng: a batch of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) with a depressed ginesenoside profile does not affect postprandial glycemia. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003 Feb; 57 (2):243-8 [PMID: 12571655]
- Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database. http://www.naturaldatabase.com. [accessed 1.29.07]
- Shanmugasundaram, E.R.B., et.al. Use of gynema slyvestre leaf extract in the control of blood glucose in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J of Etnopharmacol 1990;30:228-94 [PMID: 2259216]
- Rizvi SI, Zaid MA, Anis R, Mishra N. Protective role of tea catechins against oxidation-induced damage of type 2 diabetic erythrocytes. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005 Jan-Feb; 32 (1-2): 70-5 [PMID: 15730438]
- Anderso n RA, Polansky MM Tea enchances insulin activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2002 Nov 20; 50(24): 7182-6. [PMID: 12428980]
- Koyama Y et.al. Effects of green tea on gene expression of hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes in vivo. Planta Med. 2004 Nov; 70(11):1100-2 [PMID: 15549673]
- Han MK. Epigallocatechin gallate, a constituent of green tea, supresses cytokine-induced pancreatic beta-cell damage. Exp Mol Med. 2003 Apr 30;35(2):136-9 [PMID:12754418]
- Negrisanu G, Rosu M, Bolte B, Lefter D, Dabelea D Effects of 3-month treatment with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Rom J Intern Med. 1999 Jul-Sep;37(3):297-306 [PMID: 15532308]
- de Champlain J. et.al. Oxidative stress in hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2004 Oct-Nov; 26 (7-8): 593-601 [PMID: 15702613]
- Preuss HG, Bagchi M. Protective effects of novel niacin-bound chromium complex and a grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on advancing age and various aspecs of syndrome X. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002 May; 957:250-9. [PMID: 12074977]