Revolution C

Flavonoids and bioflavonoids, the polyphenols that accompany vitamin C in nature, are generally considered to be among the most important and interesting classes of biologically-active compounds. More than 4,000 flavonoids have been identified, having a number of functions in common with vitamin C.
Citrus bioflavonoids are commonly used in Europe for blood vessel and lymph system support. U.S. practitioners utilize bioflavonoids in protocols to manage minor pain, inflammation, and swelling, to support healthy cholesterol levels and cholesterol metabolism, to strengthen and protect collagen, and to support respiratory, eye, gum, and skeletal health.
Perhaps the most important value of the bioflavonoids, however, is their potent antioxidant capability. Equally impressive is the plentiful number of studies spanning a gamut of mechanisms by which bioflavonoids support cardiovascular health and optimal blood sugar levels.
Studies demonstrating the role of flavonoids in the prevention/anti-proliferation of many types of cancer are too numerous to cite in this reference sheet. Several mechanisms have been suggested, including direct cytotoxicity, induction of apoptosis, modulation of cell cycling, and induction of cell migration required for normal differentiated cell function.
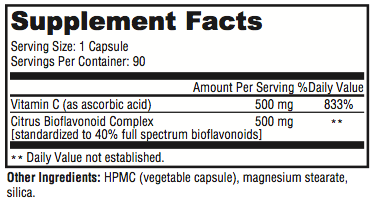
Directions
Take 1 capsule daily (unless otherwise instructed)
References
- Guardia T, Rotelli AE, Juarez AO, Pelzer LE Anti-inflammatory properties of plant flavonoids. Effects of rutin, Quercetin and hesperidin on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Farmaco. 2001 Sep;56(9):683-7. [PMID: 11680812]
- Rotelli AE, Guardia T, Juarez AO, de la Rocha NE, Pelzer LE. Comparative study of flavonoids in experimental models of inflammation. Pharmacol Res. 2003 DEC;48(6):601-6. [PMID: 14527825]
- Pijnenburg MW, Hofhuis W, Hop WC, De Jongste JC. Exhaled nitric oxide predicts asthma relapse in children with clinical asthma remission. Thorax. 2005 Mar; 60(3):215-8. [PMID: 15741438] Lee NK, Choi SH, Park SH, Park EK, Kim DH. Antiallergic activity of hesperidin is activated by intestinal microflora. Pharmacology. 2004 Aug;71(4):174-80. [PMID: 5240993]
- Ferrari CK, Torres EA. Biochemical pharmacology of functional foods and prevention of chronic diseases of aging. Biomed Pharmac other. 2003 Jul-AUG;57(5-6):251-60. [PMID: 12888262]
- Bobyrev VN, Rozkolupa NV, Skripnikova TP, [Experimental and clinical bases for the use of antioxidants as agents for treating and preventing periodontitis] Stomatologiia (Mosk). 1994 Jul-Sep;73(3):11-8 [PMID:7846703]
- Bone loss: Lin N, Sato T, Takayama Y, Mimaki Y, Sashida Y, Yano M, Ito A. Novel anti-inflammatory actions of nobiletin, a citrus polymethoxy flavonoid, on human synovial fibrolasts and mouse macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Jun 15;65(12):2065-71 [PMID: 12787887]
- Perez-Vizcaino F, et al. Endothelial function and cardiovascular disease: Effects of quercetin and wine polphenols. Free Radic Res. 2006 Oct;40(10):1054-65 [PMID: 17015250]
- Peluso MR. Flavonoids attenuate cardiovascular disease, inhibit phosphodiesterase, and modulate lipid homeostasis in adipose tissue and liver. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006 Sep; 231(8):1287-99 [PMID:16946397]
- Braganhol E, et al. Antiproliferative effect of quercetin in the human U138MG glioma cell line. Anticancer Drugs. 2006 Jul; 17(6):663-71 [PMID: 16917212]
- Rossi M, et al. Flavonoids and colorectal cancer in Italy. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006 Aug; 15 (8): 1555-8 [PMID: 16896049] http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/natural/patient-vitaminc.html {revised 10.11.06}