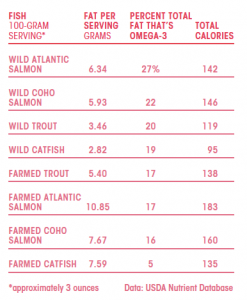
Farmed vs Wild Salmon


Updated 12/28/15:
You can read more about the flu virus itself on the ‘What Is The Flu?’ post.
It has been stated, and many people believe, that the best way to prevent the flu is to get a flu shot. That concept is a load of nonsense! This mentality is like saying the best way to keep from getting shot is to wear a bullet proof vest.
The BEST way to prevent the flu is to avoid it altogether. Unfortunately, this isn’t always possible.
When I was in Iraq, we didn’t simply wear our “bullet-proof vest” in the traditional sense. We wore trauma plates, helmets, gloves, eye protection, hearing protection, etc. We wanted as much protection as possible. This should be the concept for the flu as well. We should support the immune system from every angle and in every way possible in order to equip our bodies with everything they need to prevent illness associated with the flu.
It seems that the idea of getting a flu shot each year stimulates a lot of emotion for some people.
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve heard patients tell me that the only time they’ve gotten the flu is when they’ve received the flu shot. The best thing we can do is arm ourselves with good education on the topic and let each patient decide for themselves. As always, if the benefits outweigh the risks then go for it. However, that is NOT the case for the flu shot!
Many people believe that the flu shot is supposed to prevent them from getting the flu. It doesn’t work that way.
The intent of vaccination to build antibodies against an antigen which is presented to the body (injected, ingested, inhaled, etc). The antibodies will be able to fight the specific infection if ever exposed.
It is important to understand a little bit about the flu virus itself in order to understand the vaccine itself.
The flu vaccines are trivalent, meaning that they target 3 strains of the virus, or quadrivalent, targeting 4 different strains. Trivalent vaccines target 2 Influenza A strains (H1N1, H3N2) and 1 Influenza B strain. The quadrivalent vaccine targets 2 A’s and 2 B’s. There are 4 different types of flu shots:
The World Health Organization (WHO) receives information from the Global Influenza Surveillance & Response System which ultimately determines the strains included in the annual vaccine. High yield candidate vaccine viruses are developed by collaboration of laboratories involved in developing reassortants and WHO Collaborating Centers (CCs). National Influenza Centers (NICs) collect specimens in their country and perform antigenic characterization. These results are sent to the WHO and is the basis for recommendations for the strains included in the annual influenza vaccination. Basically, it is a guessing game…
The problem that I have is that if they determine it is a different strain than predicted then why don’t they stop giving the shot. If they are wrong then the vaccine is absolutely useless. This makes no sense! Of course, they’ll say that there is ‘cross-reactivity’ among strains of flu.
Do you wonder what is actually being injected? I think that is important to understand exactly what you are getting when you get the flu shot.
The strains of flu that are identified in Asia in the spring are cultivated in chick embryos (eggs, this is why they won’t give you the flu shot if you are allergic to eggs) for a few weeks. Then, they inactivate the virus by adding formaldehyde, the same chemical that we have used to embalm things. Finally, they add thimerosal as a preservative (in some vaccines).
What is the world is thimerosal? It is an antiseptic and antifungal that is made with mercury. I don’t want to get too deep into the thimerosal debate but the Institute of Medicine (IOM) agreed that thiomerosal could be associated with neurodegenerative diseases and that its removal from childhood vaccines was beneficial. The bottom line is that we should totally avoid mercury. Period! It is toxic stuff!
How much mercury is in thimerosal? The package inserts for flu vaccines state that it is “less than 25 mcg of mercury per dose.” So is it 1 mcg or 24.99 mcg? This is 250 times HIGHER than the safe limit set by the EPA!
There are also other toxins in some of the flu vaccines:
The flu vaccine has actually been banned by countries in the past. That should tell us something!
Potentially serious reactions to the flu shot include (but are not limited to): allergic reaction to any of the ingredients; thrombocytopenia; neurologic disorders; encephalitis; Guillain-Barre Syndrome; mercury toxicity; acute illness
Here is a picture of the package insert from one of the vaccines (Flulaval) discussing the potential risks:
If this weren’t enough to make you think twice…
The 2009 H1N1 (swine flu) outbreak brought to light another adverse effect of the traditional flu vaccine. It can actually make you MORE susceptible to a different infection. How could this happen?
Flu vaccines can be immune suppressive. They divert the immune system to produce antibodies against a specific antigen. That is what it is supposed to do… make antibodies against the virus. But this activity diverts the immune resources and can leave you susceptible to infection from another virus or bacteria. This is part of the risk you are taking when you get a flu shot. You are trading the increased risk of another infection for possible protection against the flu.
In fact, during that swine flu outbreak in 2009, those that got the seasonal flu shot were twice as likely to get swine flu.
As stated above the flu shot is a total guess. But even if they do get it right there is still no evidence that it works. Study after study reveals the same conclusion that they do not prevent people from getting the flu and they do not prevent death. There is even some evidence that it can increase the risk of death is some patients.
The issue comes down to the difference between efficacy and effectiveness. Yes, the flu shot is efficacious. This means that it does work to increase antibodies against some parts of the flu virus. However, effectiveness is very different. Effectiveness means that it would decrease flu disease but that is simply not the case. But don’t take my word for it. Here is a statement from the package insert from the flu vaccine Flulaval:
” FLULAVAL is an influenza virus vaccine indicated for active immunization of adults 18 years of age and older against influenza disease caused by influenza virus subtypes A and type B contained in the vaccine. This indication is based on immune response elicited by FLULAVAL, and there have been no controlled trials demonstrating a decrease in influenza disease after vaccination with FLULAVAL.”
Then again, I can make up anything I want and write it down so here is a picture of the actual insert:
Did you read it? It states, right there in the package, that it has NOT been proven to be effective.
I don’t know what else to say.
Interestingly, that statement has since been removed from the package insert since that time. However, you can google the package insert and it will also tell you that it contains 25 mcg of mercury. I’m not making this stuff up.
If you still have doubts about what I’m saying here then maybe this will help:
62% of healthcare workers do NOT get their flu shot!
They don’t get them for a few reasons. They include: they didn’t believe the flu shot worked; they felt that their immune system was strong enough to fight of the flu; and concern about side effects. I believe we should lead by example.
If our healthcare workers (doctors, nurses, etc) aren’t getting the flu shot then why should you? That question has been asked and there is an active movement to REQUIRE health care workers to receive the flu vaccination.
We discussed the possible mercury exposure due to the preservative thimerosol. We also discussed the fact that during the swine flu epidemic of 2009 you were twice as likely to get the swine flu. A study of the incidence of Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) following the 2009-2010 swine flu epidemic showed a 57% increased risk of GBS in those who received the vaccine. It should be noted that the incidence of GBS is very low so a 57% increased risk is still a very small number. However, this is a potentially very serious condition that simply cannot be minimized.
You can read more on this post, or this post.
So, the risks of the flu shot may outweigh the benefits. The CDC says that the best thing you can do to prevent the flu is get the flu shot.
If that isn’t true then what should you do? Read the post on How To Prevent & Treat The Flu.
Come to Revolution Health with Tulsa Thyroid Problems
This Content Was Written by Revolution Health
When coming into Revolution Health you’ll find we are very helpful when it comes to any type of problem you might be having. If you’re drinking Tulsa thyroid problems there’s no doubt we can help you right here in our office. You can find Revolution Health at 2865 East Skelly Dr. 300 Tulsa Oklahoma. You can also reach us by phone at 918-935-3636. We’re always looking for to meet with her new clients in helping them with whatever problems they might have. Give us a call today or go online for website at www.revolutionhealth.org to find out more about what we can offer you.
There are a few ways you can determine if you are having thyroid problems. We like to look at three major things we believe are going to be very important when it comes to determining if you are having a problem with your thyroid glands. We believe it is very important for you to catch the services and get started on your Tulsa thyroid treatments as quickly as possible. You may notice that here at Revolution Health we try to take a more holistic approach. You’re sure to get a great healthy way to recover from your thyroid problems and get great treatments here Revolution Health. We’re always looking for ways to help our patients recover from their problems to provide them with great solutions to picking get on with your life in a healthy way.
The first signs you might have a thyroid problem you need to seek treatment is going to be neck discomfort and enlargement. If you’re feeling of your neck and swelling in your having some slight discomfort whether it’s with your shirts, or neckties or maybe even have a horse boys distribute telltale sign of an enlarged thyroid gland. We have an enlarged thyroid gland is can be a symptom of thyroid disease. You may also do a thyroid neck check at home just to make sure. Would also like you come in to Revolution Health and see what we can do to help you with your thyroid.
One of the things that many people do not think about it comes to their thyroid problems is what is going to be particularly vulnerable. When it comes to hair and skin you’ll be surprised how vulnerable the two parts of your body can be. When it comes to hypothyroidism the hair becomes brittle health and driving course. You can fallout easy or break off. This is the same when it comes to skin. The symptoms can often be a sign of hypothyroidism and you should really come into the revolution health office to get you down.
Last a sign that we look for our your weight changes. This often occurs if you’re a low-fat look to diet with it great exercise program you are feeling to lose the weight or gain any weight for that matter. If you’re on a strict diet and a strong workout program and are nothing changes you should be seeing this could be a sign of hypothyroidism. When it comes to unexplained weight changes this can often be signs of hypothyroidism or other thyroid problems. With its hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism is very important you seek treatment as soon as possible. You’ll find Revolution Health is very helpful when it comes to solving your Tulsa thyroid problems with our great Tulsa thyroid treatments.
Tulsa Thyroid Problems
This Content Was Written by the Revolution Health
When it comes to finding out if you have Tulsa thyroid problems we highly recommend you come in to see Doctor Edwards. Doctor Edwards can be found at Revolution Health right here at 2865 East Skelly Dr. number 300 and Tulsa Oklahoma. Doctor Chad Edwards, D.O. is been providing preventive medicine since 1989. He’s going to be sure to provide you with solutions to your Tulsa thyroid problems and get you the Tulsa thyroid treatments that you are going to require. We take it upon ourselves to help you in a holistic way to your body to naturally recover on its own. Give us a call today at 918-935-3636 and was started on can solutions to your thyroid problems.
One of the ways we try to help our patients bodies recover from their ailments is by providing with stimulation in certain areas. One way to do this is through supplementation. We not believe in providing you with 10 different kinds of medications for you to take every day, three times a day. We leave provide you with all-natural supplements that are going to help your body stimulate certain areas that are going to help you recover from certain problems. At Revolution Health you’re going to get a natural way for you to recover from any type of injury or ailment you might have.
Here at Revolution Health we believe that we are in dire need for revolution in this country. Italy that we do not you move towards an approach is going to recommend medication is the sole solution for any medical problem. With our solutions to your problems you are guaranteed to get a great way for you to recover from your injuries. Whether you’re suffering from Tulsa thyroid problem and are looking to get Tulsa thyroid treatments we highly recommend you come into the Revolution Health office today. You’ll find we’re going to be very courteous and help you solve the issues one step at a time.
When it comes Tulsa thyroid palms there are a few ways you can determine if you have something wrong with your thyroid. The firewood is a small gland that is shaped like a butterfly located just under the Adam’s apple. This is in the lower, front part of the neck victory to problems that can arise when it comes to your thyroid. The first is hypothyroidism. This happens when the gland is underactive. Maybe it did not form properly of birth, surgically removed or is become incapable of producing enough of the thyroid hormone is most be produced. This can result in a slowdown of your metabolism.
Second problem that could arise is going to be hypothyroidism. This is just the opposite of hypothyroidism. This is when the thyroid is overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. The majority of the dysfunctions such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are caused from autoimmune thyroid disease. The Revolution Health we’re going to try and provide you with a systematic approach is going to allow you to recover from this ordeal with this in a natural way. At Revolution Health we’re going to provide you with knowledgeable solutions to your thyroid problems. Give us a call today at 918-935-3636 or online for website to find out more information about what we can do to help you.
The Bressler Report points out the blatantly false information presented by G.D Searle in trying to get aspartame approved by the FDA. I have full report here: Bressler Report on Aspartame
 Adiponectin
AdiponectinAdiponectin is a hormone that is excreted exclusively from adipose (fat) cell and helps regulate several metabolic processes including the oxidation of fatty acids and glucose regulation. Levels are inversely correlated to the amount of body fat. In other words, if you have more body fat then your adiponectin levels should be lower.
Adiponectin plays a role in suppressing the metabolic dysfunction that often leads to metabolic syndrome, Diabetes (type 2), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), obesity, and atherosclerosis. To underscore its role in regulating metabolism, adiponectin in conjunction with leptin was able to completely reverse insulin resistance in mice.
Adiponectin levels are generally higher in females than in males. Body fat reduction greatly increases serum levels of adiponectin. Diabetics have lower levels of adiponectin than non-diabetics. Obesity and TNF-a (an inflammatory marker) both decrease adiponectin levels. Low adiponectin is an independent risk factor for developing diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Molecules of adiponectin tend to join together to form polymers of adiponectin. These larger molecules seem to be the most active in regards to appropriate maintenance of glucose but this form is also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). At least some of the weight reduction effects of adiponectin occur in the brain and seems to work synergistically with Leptin in this regard.
Adiponectin has the following effects:
Interestingly, levels of adiponectin were disproportionately elevated in the blood of patients who went on to develop Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) as noted in the Framingham Heart Study. This information suggests that elevated levels of adiponectin could cause Alzheimer’s Disease. However, while we don’t know the answer to this piece, there are other potential explanations such as adiponectin resistance. For example, elevated insulin levels do not cause diabetes but are the result of insulin resistance that accompanies diabetes. This could be the same explanation for the development of AD in the setting of increased adiponectin levels.
Berberine & Omega-3s have all been shown to increase the genetic expression of adiponectin. Curcumin, Resveratrol, astaxanthin, exercise, and Vitamin D (possibly) have been shown to increase adiponectin. The best options for improving adiponectin are supplements as listed above as well as optimizing body composition, decreasing body fat, exercising, and eating right.
Adipose (fat) tissue has a number of functions. In addition to its role as a storage form of energy, adipose tissue is a highly active endocrine organ that coordinates multiple hormonal, metabolic, inflammatory, and neurohumoral activities.1,2 Adipocytes produce and secrete a variety of bioactive proteins into the bloodstream, collectively called adipocytokines, including leptin, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and other cytokines, plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1), resistin, apelin, retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4), and adiponectin.2
Adiponectin is a 247-amino-acid protein produced almost exclusively by adipocytes, although low level expression can also be detected in skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and liver.3,4 It belongs to the collagen superfamily and exists either as a full-length 30 kDa protein or as smaller globular fragments, with the full-length monomer produced primarily by adipocytes.2,3
Circulating adiponectin monomers assemble to form several multimeric forms, including high-molecular weight (MW) oligomers, a medium-MW hexamer, and low-MW trimer. The different multimeric forms individually range in concentration from 2-30 μg/mL in the bloodstream, and may exert different biological actions.5-7 Adiponectin plays an important role in both insulin action and cardiovascular health. Cellular actions of adiponectin are mediated via specific receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2.8
AdipoR1 are expressed ubiquitously, with particularly high levels in skeletal muscle, while AdipoR2 expression occurs predominantly in liver.8 Both receptors are expressed in cardiac tissue.9 Both AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 activate the APPL1-AMP kinase signaling cassette in different tissues.
Adiponectin-mediated AMPK activation leads to suppression of gluconeogenic enzymes in liver and enhances fatty acid β-oxidation in both liver and muscle, counteracting the lipotoxic effects of obesity and type-2 diabetes that lead to insulin resistance in those tissues.10 Adiponectin may also directly enhance GLUT4 translocation in muscle via APPL1 signaling.11,12
In addition, adiponectin exerts protective cardiovascular effects by enhancing endothelial function and inhibiting atherogenesis through multiple mechanisms.13,14 In the heart, adiponectin helps to prevent left ventricular hypertrophy and ischemia-reperfusion injury, and enhances healthy myocardial remodeling in the post-MI period. Recent evidence suggests that adiponectin may also support the function and longevity of pancreatic β cells.15
Adiponectin testing is performed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), with risk ranges:
Clinical and experimental studies show that low concentrations of adiponectin (hypoadiponectinemia) may contribute to type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disease. Decreased plasma adiponectin levels occur in genetic and diet-induced rodent models of obesity, as well as in human diseases associated with insulin resistance.16-19 This is in contrast to most other adipocytokines, whose levels are increased in these conditions, often in proportion to increased fat mass.
In cross-sectional studies, adiponectin has consistently been correlated with elements of the metabolic syndrome: plasma levels decrease as abdominal adiposity, plasma glucose, HbA1C, and measurements of insulin resistance increase.6 Recent studies have demonstrated that adiponectin may be one of most consistently reliable indicators of risk for incident type 2 diabetes among nondiabetic individuals. Importantly, the association of adiponectin with type-2 diabetes risk is independent of most other traditional risks, including age, family history of type-2 diabetes, height, waist circumference, resting heart rate, hypertension, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting glucose and serum uric acid.20
Euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp studies in both humans and rats demonstrate that insulin itself can exert an acute effect to suppress adiponectin production by adipocytes; therefore chronic hyperinsulinemia may be an important factor leading to reduced adiponectin production in insulin-resistant states.21 In addition, certain genetic polymorphisms of the adiponectin gene that affect protein expression may contribute to reduced adiponectin levels and increased risk for type-2 diabetes.22,23 Men generally have lower adiponectin levels than women, possibly due to androgen effects21,24,25 and levels are also influenced by ethnicity.25
Recent large trials demonstrate that adiponectin levels are also an important indicator of risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality.26 Low adiponectin adds risk that is independent of all other traditional cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., Framingham and Reynolds-type risk) and quantitative in nature: one study demonstrated a step-wise 20% increase in cardiovascular events/death for every 5 ug/mL reduction in plasma adiponectin levels.
These findings confirm an extensive prior body of knowledge from smaller studies in which adiponectin has been associated with different aspects of increased cardiovascular risk. Plasma adiponectin levels are lower in diabetic patients who also have coronary artery disease (CAD) than in those without CAD, indicating that adiponectin may have anti-atherogenic properties.27 The incidence of cardiovascular death has also been found to be higher in patients with renal failure who have low adiponectin levels, indicating that the relationship remains valid even when renal function may be impaired.24,28
Adiponectin inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth cells and is abundant in the vascular intima of catheter injured vessels.29,30 Adiponectin decreases the surface expression of vascular adhesion molecules that modulate endothelial inflammatory responses and suppresses macrophage-foam cell transformation in vitro.29,31
Consistent with its anti-inflammatory actions, adiponectin concentrations are inversely correlated to high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP; a marker of inflammation) and coronary atherosclerosis.20 Importantly, adiponectin appears to protect against myocardial infarction, independently of CRP or glycemic status in patients with atherosclerosis.32,33
In other clinical studies, low adiponectin levels have been associated with essential hypertension and an atherogenic lipid profile.27,34,35 Adiponectin influences plasma lipoprotein profiles by altering the levels and activity of key enzymes (lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase) responsible for the catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), thus influencing atherosclerosis by affecting the balance of atherogenic and anti-atherogenic lipoproteins in plasma. Several studies have reported a significant negative correlation between circulating adiponectin and triglyceride levels, and a positive correlation between adiponectin and HDL cholesterol (HDL-C), in both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals.6,27,34
There is increasing evidence to support the notion that adiponectin not only has diagnostic/prognostic value but should also be considered a therapeutic target.36-38 Since a decrease in adiponectin levels may precede development of other markers of insulin resistance, early initiation of therapy could potentially halt or reverse the progression of metabolic or cardiovascular disease associated with low adiponectin.
Lifestyle modification, visceral fat reduction, and certain medications can both increase serum adiponectin levels and improve insulin sensitivity, thus helping to prevent both type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.2 Certain lipid-lowering drugs, such as niacin and fibrates— which primarily lower triglycerides and increase HDL-C level— also increase adiponectin levels, typically in proportion to the extent of change in HDL-C and triglycerides. In general, thiazolidinedione peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma agonists (e.g., pioglitazone or Actos) increase adipocyte adiponectin production and circulating adiponectin levels. However, it is not known whether this benefit outweighs some of the cardiac risks associated with thiazolidinediones. Specific agonists of adiponectin receptors are currently in preclinical phases of development.6,39,40
If FPG and HbA1c are abnormal, follow therapeutic guidelines of the American Diabetes Association. The following lifestyle recommendations and medications can be used to reduce insulin resistance and improve β-cell function, personalized to the individual patient’s clinical needs.
NOTE: No medications are currently FDA approved for the treatment of insulin resistance or β-cell dysfunction. Insulin may be considered for the treatment of hyperglycemia meeting ADA criteria for diabetes but should NOT be used in the setting of insulin resistance without diabetes or in prediabetes due to the potential for hypoglycemia.48 Patients who are taking metformin are at increased risk for vitamin B12 deficiency and may benefit from sublingual vitamin B12 supplementation.49
posting thoughts on stuff
Do you have low back pain or neck pain and been told that your pain is due to a herniated disk? Have you been told that surgery is your only option for treating your pain?
We have news for you… there may be another option that you may not have heard of before!
Prolotherapy can improve function and decrease back pain associated with herniated disk disease in many cases.
In order to understand how prolotherapy can help this problem we have to understand the problem itself. The spinal column is composed of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae (fused), and the coccyx. There is a bony joint called the facet which connects one vertebrae to the one below. There are 2 facets per segment. These joints are held together by ligaments that form the joint capsule.
In between these vertebral segments is an inter-vertebral disk. The disk is composed of a tough outer ‘shell’ made of collagen called the annulus fibrosis. Within the outer shell is the ‘jelly filled center’ called the nucleus pulposus. The disk serves as a shock absorber and cushion.
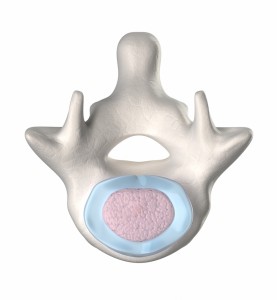
The weakest spot of the disk is the back side. There is a tough ligament, the posterior longitudinal ligament, that covers much of the posterior portion of the disk leaving the posterior corners the most vulnerable and this is exactly where disk herniation generally occurs.
Additionally, the spinal nerves leave the spinal canal through the intervertebral foramen. The weak spot of the disk generally corresponds to the area where this nerve exits the foramen and can compress it resulting in ‘radiculopathy’. Surgery for herniated disks involves surgically repairing the disk and decompressing the nerve resulting is elimination of radiculopathy.
One source states that the surgery SHOULD be 95% effective in eliminating the radiculopathy. However, they also state that 10% of patients will have a recurrence in the same area and require repeat surgery. They recommend a spinal fusion if this occurs repetitively.
I have a few issues with this approach.
First, not all “pain going down my leg” is due to a herniated disk, even if you find a herniated disk on MRI. Several studies have been performed that raise questions on whether or not we can accurately attribute an abnormal finding on MRI to the cause of the symptoms. Back pain should be evaluated by a trained prolotherapist before any surgery is considered (unless it is a true emergency) because there are other potential causes for pain going down the leg besides herniated disks.
Next, we need to evaluate the actual cause of the herniated disk. Have you ever wondered WHY these things occur in the first place? I don’t believe they ‘just happen’. Here’s how I believe these things get started…
Step 1: There is damage to the ligaments that form the facet joint capsule allowing excess movement and flexion.
Step 2: Excess flexion causes increased stress on the disk but also increases the stress exponentially on the anterior column (the front edge of the disk) and forces pressure posteriorly along the weakest area of the disk. This allows the disk herniation.
If I am right, we can help this problem with prolotherapy on the spinal facets which will tighten up these joints, restore proper spinal function, and provide an environment for the disk to heal itself.
Here is an example.
A 53 year old active duty Marine Corps Master Gunnery Sergeant with a history of repetitive low back pain after a sports injury 10 years prior. He was told that he had disk rupture with stenosis and surgery was recommended. He underwent 1 year of physical therapy and other conservative therapies and had no improvement and his left leg started hurting. He stated that his pain was getting worse and it hurt to sit and lay down.
An MRI was obtained and is shown below:
June 14, 2010 – the patient received his 1st prolotherapy procedure with standard proliferant solution.
July 30, 2010 – the patients states that he has no back pain but does have some left buttock and radiating pain to the top side of his foot from 1 week prior. He received his 2nd round of prolotherapy with dextrose and added PRP at this time.
August 27 & October 2, 2010 – prolotherapy & PRP (#3 & #4). He has no back pain with only mild pain on the dorsum of his foot. He states that he is more than 90% improved at this point.
November 13, 2010 – he states he has almost no pain and he received his 5th prolotherapy procedure.
April 8, 2010 – he returned to the Army Hospital and saw his orthopedic surgeon who told him “you can’t cure ruptured disks and spinal stenosis with an injection” and that this was “nonsense!” The surgeon wanted to “prove this nonsense” with a follow up MRI.
The comparison of the before and after MRIs are below. The herniation is depicted by the arrows.
The surgeon was surprised by this MRI finding and had to admit the success. The patient stated that he had no problems with tough military training.
This case underscores the potential benefit of prolotherapy with a specific injury. We have tremendous success with treating low back pain with prolotherapy in our clinic and would love to help you with your pain.
Consider the cost of surgery: time off from work, family, and exercise; physical therapy; medications; and potential risks.
Now consider the cost of prolotherapy: no time off of work; limited recovery needed; no medications (generally); and very low risks.
The choice is clear. Contact us to schedule your prolotherapy evaluation today!

Injury goes hand-in-hand with sports and athletics and the more intense the sports or athletics the more common and intense the injury potential. The injuries vary from overuse & overtraining to torn muscles, ligaments, meniscus, herniated disks, labrums, etc.
Every CrossFit athlete’s goal (that we’ve seen anyway) is to increase their health, fitness, strength, endurance, power, etc as much as possible. Therefore, they push the limits on what their body can handle. This makes injury a more common entity.
The goal of every CrossFit box, trainers, etc is to keep these athletes in the gym and to increase the performance of their athletes. The goal of Revolution Health & Wellness Clinic is to keep our patients as healthy and fit as possible. Thus, we share the same goal of these athletes, trainers, owners, etc. We want to prevent injury as much as possible but when injury does occur we want to fix it as quickly as possible so that these athletes can resume optimal fitness and performance.
I was an Athletic Trainer in college and worked with athletes and their injuries. My training, at that time, was the standard dogma of “R.I.C.E.” or Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation as initial therapy for most injuries. In fact, we literally had T-shirts that simply said “Just Ice It.” This was generally followed by motrin, naprosyn, etc for the pain and swelling. Motrin is often called “Ranger Candy” in the Army due to its frequency of use for “all that ails you.”
R.I.C.E. therapy and NSAIDs (Anti-Inflammatory medications) serve to decrease the symptoms (pain & swelling) after an injury but they DO NOT help to heal the injured areas sooner. In fact, they can be very detrimental and actually slow or even stop the healing process. It is a faustian bargain!
Since our goal is to get these athletes back as quickly as possible, we want to find an intervention that heals the damaged tissues faster and produces better, stronger, and thicker ligaments and tendons. In short, we want the CrossFit approach of healing.
Prolotherapy stimulates more rapid and complete healing. In fact, studies performed in the 1950’s showed that prolotherapy increases the diameter of the injected ligaments by up to 40%, increases the attachment area to the bone by 30%, and increases the strength of the ligament by 50%.
If you have been reading our information on Prolotherapy then you know that most causes of musculoskeletal pain can find its roots in ligament and/or tendon relaxation or damage. Relaxed ligaments and tendons will not show up on an MRI and are a common cause of “unexplained pain” with normal radiologic studies. Additionally, an abnormal finding on MRI doesn’t mean that the abnormality is the cause of the pain or problem.
I have seen numerous soldiers and other patients with extremely painful conditions but nobody could identify why. They are generally referred to surgical procedures (without improvement by the way), physical therapy, pain management, etc. Who wants that?
The optimal treatment is to RESTORE NORMAL ANATOMY AND FUNCTION!
When ligament and tendon relaxation is the cause of pain then the only therapy is prolotherapy! Unfortunately, the art of physical exam for ligament and tendon damage as been lost with the advent of more expensive testing such as CT & MRI which cannot accurately evaluate these structures as the source of pain anyway!
We treat CrossFit athletes every day with minor and significant injuries. We have had the honor of treating several nationally competitive CrossFit athletes and had excellent results. We have been able to reduce pain, improve performance, and return them to full function sooner than any other therapy we’ve seen.
If you are a CrossFit athlete (or if you know one) then you should have a prolotherapy physician’s information stored in your phone. You should have their phone number in your rolodex. You should have their information posted in your gym.
We all have the same goal. Let us help you achieve it!
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is a lipoprotein that is found in Chylomicrons and Intermediate Density Lipoproteins (IDLs) and transports fat-soluble vitamins, cholesterol, and lipoproteins into the blood via the lymphatic system. The receptors for ApoE are in the LDL receptor family.
ApoE defects are associated with Type III hyperlipoproteinemia (familial dysbetalipoproteinemia) where an increase in serum cholesterol & triglycerides are caused by decreased clearance of chylomicron, VLDL, and LDL remnants.
Alzheimer’s Disease – The exact mechanism of how E4 causes such dramatic effects on Alzheimer’s Disease risk remains to be fully determined. However, evidence has been presented suggesting an interaction with amyloid. Alzheimer’s Disease is characterized by build-ups of aggregates of the peptide beta-amyloid. Apolipoprotein E enhances the break-down of this peptide, both within and between cells. E4 is not as efficient at catalyzing this proteolytic break-down which causes an increase in risk to Alzheimer’s Disease.
Although 40-65% of AD patients have at least one copy of the 4 allele, ApoE4 is not a determinant of Alzheimer’s Disease – at least a third of patients with AD are E4 negative and some E4 homozygotes never develop the disease. Yet those with two E4 alleles have up to 20 times the risk of developing AD.
There is evidence that E2 may protect against AD. Thus, the genotype most at risk for Alzheimer’s disease and at earlier age is ApoE 4,4. The E3/E4 genotype is at increased risk, though not to the degree that those homozygous for E 4 are. E3/E3 is considered at normal risk for Alzheimer’s disease. The genotype E2/E3 is considered at less risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Interestingly, people with E2/E4 are at normal risk similar to the E3/E3 genotype.
There is evidence that ApoE may suppress T cell proliferation, macrophage function regulation, lipid antigen presentation facilitation to NK T cells and modulate oxidation & inflammation.
There are 3 different forms of Apo E:

That is where Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy comes in.
PRP has been around for several years and has more support in the medical literature. The rational for this is quite simple. The machines & systems used in order to obtain the platelet rich plasma portion of the blood are proprietary and there is money in selling the machines and kits for PRP. Thus, these medical device companies have a vested interest in equipment sales. Therefore, the greater the demand for PRP the more devices they will sell. Any time there is money there can be research studies to back it up!
The procedure for PRP is essentially the same as for prolotherapy. We are stimulating the immune system to heal itself. The primary difference is in the type of proliferant solution. PRP uses the platelet rich portion of plasma once the blood has been ‘spun’ to separate the components.
Platelets are very small cell components that critically contribute to the healing process. As the body’s primary source of bioactive tissue growth factors, platelets include:
By concentrating these growth factors and injecting them at the site of injury, the body’s own stem cells are drawn to the injured area and differentiate to form new healthy and robust regeneration of damaged ligaments and tendons.
PRP does seem to be a bit more potent in stimulating the inflammatory response. The pain after the procedure also seems to be a bit more intense as well.
For those that want to see the process of PRP, here you go…
MSC’s are multi-potent stem cells that can transform into several of types of cell during the tissue repairing process. The different types of cells that MSC’s have been known to transform into include collagen secreting cells, bone forming osteoblasts and cartilage forming chondrocytes. Collectively, all of these cells can potentially rejuvenate tissues that have been damaged due to injury, osteoarthritis and degenerative changes.
The platelet rich plasma process concentrates fibrin, mesenchymal stem cells and platelets so that each cubic millimeter of the solution consists of 1.5 to 2 million platelets. This results in up to a five-fold increase in the platelets and bioactive growth factors. Platelet Rich Plasma acts as a tissue growth accelerator which amplifies the natural process of the tissue reparation and healing, due to its potency. Studies have revealed that PRP stimulates not only the production of new collagen at the fibroblasts, but bone and cartilage cells at the site of the injection. This strengthens injured ligaments and tendons by rebuilding the joint cartilage. This new, strong, collagen is naturally incorporated into the existing cartilage and ligaments making them thicker and more elastic.
Cortisone injections actually weakens tissue. Although cortisone injections have been known to provide temporary relief and to stop inflammation, they do not provide long-term healing. The process of Platelet Rich Plasma therapy heals and strengthens the tendons and ligaments, in some cases thickening the tissue up to 40%.
When regular dextrose prolotherapy has provided positive results but recovery has not been ideal, PRP Regenerative Injection Therapy is especially useful. In these types of situations PRP is often the treatment option that will resolve the less responsive or more injured areas. In fact, clinical and anecdotal experience has demonstrated that using PRP as the prolotherapy injection solution creates a deeper healing effect and results in an accelerated healing process in fewer treatments than the regular dextrose prolotherapy..
Usually patients feel the benefits of PRP injection therapy after only two treatments. Sometimes satisfactory results may occur even sooner, however this is not absolutely certain. Although individual responses to the treatment do vary, most people require 3-6 sets of injections. Each treatment is spaced four to six weeks apart.
Because of the high success of normal Dextrose Prolotherapy, PRP is not something we normally think of as a first line solution. For really, really, bad tears or injuries, especially if someone has had some Prolotherapy elsewhere, it may be used as a first-line therapy. Because of the greater cost of PRP due to the cost of filters and PRP technology as well as preparation it is preferable to begin with regular prolotherapy as it provides excellent results 80% of the time. For those who do get PRP solution as their Prolotherapy solution, we typically see them for follow-up in four to six weeks. Generally, people know by the second PRP Prolotherapy whether it will work or not. Overall the results have been extremely positive. It is very safe. There have been no reactions related to the solution.
If you looked at the Electron Transport System (ETS) then you know that oxygen is essential for adequate energy production. It accepts the electrons generated in glycolysis and Kreb’s. However, oxygen can also be detrimental. It is the primary cause of aging.
Free radicals are produced from exposure to one of several factors. Inflammation, radiation (i.e. x-rays), aging, high pO2, smog (such as ozone or NO2), re-perfusion injury, and chemicals and drugs can all produce free radicals. Additionally, free radicals are produced as a part of normal metabolism.
For roughly every 26 molecules of oxygen reduced in the ETS, one free radical is produced.
A free radical is an unstable molecule that has an “extra” electron. The molecule is eager to donate its electron to any molecule that will accept it. The accepting molecules can be any number of molecules such as those that compose cell membranes. These extra electrons are damaging to the accepting substances.
In fact, aging has been attributed to oxidative damage. Atherosclerosis may also accurately blame itself on oxidative damage.
To give you an idea about how lethal these reactive oxygen species can be, white blood cells use them as their killing agents. It is what they use to kill and destroy anything that they engulf.
Pretty powerful stuff.
Free radicals are also known as reactive oxygen species. Some of these reactive oxygen species are:
Harbor-Weiss Reaction
O2 + e- -> O2- + e- + 2 H+ -> H2O2 + e- + H+ -> OH·
I put in that reaction to show how some of these molecules can be produced. During infection, WBC’s undergo what is referred to as a respiratory burst. This burst produces more OH· molecules in order to have the firepower to destroy the invading organism.
We’ve already discussed how some of these things can be formed. If we didn’t have any protective mechanisms, we would probably be destroyed as well. Well, we are but the process takes much longer due to protective mechanisms. We talked about how normal metabolism (respiration) produces free radicals.
Anything that increases the need for oxygen increases free radical production. Exercise increases oxygen utilization and, ultimately, free radical production. How, then, can exercise be beneficial? The answer is in the protective mechanisms.
There are three sources of enzymatic defense: superoxide dismutase; catalase; and glutathione peroxidase.
So we have three enzymes that provide protection against reactive oxygen species (free radicals). That doesn’t answer the exercise question.
Exercise increases the function of these enzymes. Exercise increases the production of free radicals but also increases the protective enzymes. It would seem that these two balance each other out and exercise would be a mute point. However, exercise is short term while the increased activity of the protective enzymes lasts longer. Thus, exercise has a protective role in reducing free radical damage.
Another source of protection is from free radical scavengers (anti-oxidants). There are several chemicals that are known to have anti-oxidant properties.
These substances accept the electron and allow themselves to be damaged instead of the cells. These substances can then be safely excreted. However, if you don’t have enough of these substances, your cells take the hit.
Nutritional antioxidant supplementation effectively decreases oxidative stress and can prevent much of this damage.
Cholesterol is an essential component for life and health.
But why do we care about cholesterol levels in the first place? What difference does it make?
We care because cholesterol patterns may indicate higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Our goal is to decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease.
However, cholesterol is not now, nor has it ever been, the issue!
You may have had your “cholesterol” checked as part of a wellness exam. The reality is that you have had your lipoproteins checked.
Total Cholesterol (TC) – this is the total cholesterol measured on a cholesterol or lipid panel. Mainstream medical recommendations are that TC is <200. However, total cholesterol is not a risk factor for disease. Don’t be concerned about this value!
Triglycerides (TG) – also known as triacylglycerol. These are 3 fatty acids attached to a glycerol backbone. This is how fats are transported in the blood. Recall that blood is largely composed of water. Water & oil (fat) don’t mix. Lipoproteins enable transportation of TGs in the watery environment of blood and carry them to their destination. The goal for TG is certainly <200 but we would like <150. I argue that it is actually an indicator of other problems that increase risk and doesn’t increase risk in and of itself.
Understand that when we are checking your “cholesterol” we are not really checking your cholesterol. We are actually measuring your lipoproteins. Fats and cholesterol do not mix with water (blood) and have to be carried in a lipoprotein molecule. We classify these lipoprotein particles based on their composition. The largest of these are the chylomicrons followed by very low-density lipoproteins, LDL, and then HDL. The density was originally defined by ultracentrifugation and is determined by the composition of the molecule. The composition of each of these molecules is determined by the proteins (apolipoproteins) on the membrane of the molecule.
Chylomicrons are composed primarily of triglycerides (85%) but also contain 3% cholesterol esters, 2% cholesterol, and 8% phospholipids. They are the primary transporters of fats after fatty meals.
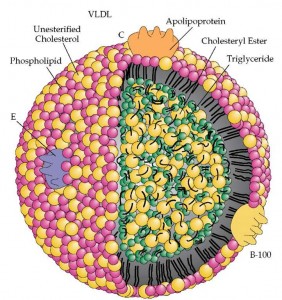 Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL)
Low-Density Lipoproteins (LDL)LDL is traditionally referred to as the ‘bad’ cholesterol. It is called ‘low density’ because it is composed of a larger amount of TGs. The traditional goal for LDL for standard risk patients is 130 or less. However, small-dense LDL (sdLDL) may be a better indicator of risk of cardiovascular disease. LDL particle number may be the best indicator of cardiovascular disease risk. The goal is to decrease the risk of small, dense LDL particle. 2 things are responsible for increasing small, dense LDL particle: genetics (nothing you can do about that) and carbohydrates. If you want to decrease your risk of cardiovascular disease, decrease your carbohydrates! Read this article for more information.
these are what has been referred to as the ‘good’ cholesterol. HDL seems to play an increasingly important role as an indicator of reducing cardiovascular risk. Normal values are typically between 35 and 70. HDL is anti-inflammatory and functions to pick up cholesterol from the peripheral tissues and transport it back to the liver (Reverse Cholesterol Transport – see below).
Non-HDL-c is simply calculated from subtracting HDL from Total Cholesterol. It is everything except the HDL. Non-HDL-c is suggested to be better correlated with cardiovascular disease. In other words, it seems to be a better risk predictor.
Goal – < 130 mg/dL
What to do about it – improve overall health using the ‘Healthy Trinity’
ApoB is the protein attached to the LDL molecule. It is the scientifically accepted measurement of atherogenic particle number. ApoB traverses in the blood in a 1:1 ratio with chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL and Lp(a). Several studies identified elevated ApoB concentrations to be highly predictive of cardiovascular events. Most studies have found ApoB to be a more reliable indicator of cardiovascular event risk than LDL-C.
Goal – < 60 mg/dL, < 55 mg/dL with CHD & CHD risk equivalents
What to do to improve it –
This is the actual number of particles of LDL measured in the sample. It is determined by NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance). Studies have shown that elevated LDL particle concentration is associated with increased risk for coronary heart disease, even in the presence of optimal LDL cholesterol values.
Goal – < 1000 nmol/L
What to do to improve it – Focus on the ‘Healthy Trinity’
Small LDL particles may be observed in association with the metabolic syndrome and pre-diabetes. Statins, while they can lower the number of LDL particles, do not change the size of the LDL particles. sdLDL is commonly present in insulin resistant patients. The small size of LDL particles enhances endothelial penetration and accelerates atherosclerosis and lipoprotein oxidation. It is associated with a 3x increased risk of MI & stroke.
Goal – < 21 mg/dL
What to do to improve it – Focus on the ‘Healthy Trinity’ and specifically blood sugar control. We recommend Wheat Belly by Dr William Davis for more information on this topic. Smoking cessation, exercise, dietary restrictions, weight loss (as appropriate), and moderate alcohol intake can impact sdLDL as well.
This is a percentage. It is how much small, dense LDL there is as a percentage of the total amount of LDL. It is mathematically derived.
Goal – < 13%
What to do to improve it – Do the same things stated above for sdLDL.
ApoA-1 is the protein associated with the HDL molecule. It corresponds with the ApoB on the LDL molecule. Low levels suggest low cholesterol clearance. When ApoA1 is low there is a 3x increased risk of MI & stroke.
Goal – > 131 mg/dL
What to do to improve it – improve overall health & HDL
Total HDL particle decrease has been associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease. HDL particle concentration may be increased with exercise, fish oil, niacin, fibric acids, or moderate consumption of alcohol.
Goal – > 35.0 μmol/L
What to do to improve it – as above
HDL2 is the largest of the HDL molecules and is the one responsible for the majority of the Reverse Cholesterol Transport. It seems to indicate greater protection and may be a marker for plaque regression. It is thought to have anti-oxidant properties. When HDL2-C is low it suggests a 2-3x increased risk of CVD.
Goal – > 12 mg/dL
What to do to improve it – as above
Recently large case control studies have demonstrated that the Apo B:Apo A-I ratio is superior to cholesterol measures and cholesterol ratios for predicting risk for myocardial infarction. In the Interheart study, comparing 12,461 myocardial infarction cases to 14,637 age and gender matched controls in 52 countries, the Apo B:Apo A-I ratio was vastly superior to any of the cholesterol parameters measured including the LDL cholesterol: HDL cholesterol ratio and the total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio in all ethnic groups, in both sexes, and at all ages.
Decreasing the Apo B:Apo A-I ratio can be achieved by lowering Apo B and/or by increasing Apo A-I.
Goal – < 0.6
What to do to improve it – focus on the ‘Health Trinity’ as primary intervention. Niacin and fibrin acids have also been demonstrated to increase ApoA1.
This is an LDL particle containing an abnormal protein. It is an inherited abnormality and elevated levels are associated with an increased risk of developing coronary artery disease. Its structure is similar to plasminogen and it competes with plasminogen for receptor sites which causes reduced fibrinolysis and increased hypercoagulability.
Goal – < 30 mg/dL
What to do to improve it –
When Lp(a) mass is > 30 mg/dL we reflexively measure the Lp(a) cholesterol. This helps eliminate false positives that result from the Lp(a) mass immunoassay. Such false positives are due to over-estimation of large species with high numbers of kringle repeats. Lp(a) elevation suggests a 3-5x increased risk of CVD.
Goal – < 2 mg/dL
What to do to improve it – Niacin, lifestyle
ApoB –
High LDL particle and/or low HDL is a risk factor for heart attacks and strokes. Treatment (according to the ATP III guidelines) is geared toward lowering LDL first and then focusing on TGs and HDL (generally).
However, the goal of therapy should be to decrease cardiovascular disease risk in general. People don’t have heart attacks because they have a Lipitor deficiency! They have heart attacks due to the effects of their lifestyle coupled with their genetics.
The best thing you can do to decrease your risk of cardiovascular disease is NOT to take a medicine! The best thing you can do is optimize your health through the ‘Healthy Trinity’ (nutrition, exercise, and rest).
__________________________________________________________________________
Here are some videos about the possibility that cholesterol does NOT cause heart disease.
As I’ve said a million times:
You can take medicines all day long but unless you attempt to improve your HEALTH then you are just taking a bunch of pills!
I used to subscribe to the NCEP Guidelines for the evaluation and management of cholesterol but not any longer. The evidence supporting these guidelines is entirely substandard!
Saturated fat has caused this problem. My grandparents ate loads of saturated fat and lived a long life. I don’t believe that people have ‘elevated cholesterol’ because they have a deficiency of soluble fiber, plant stanols/sterols, medications (statins), or eat too much cholesterol. There may be an improvement in lipid panels if you implement the ‘TLC diet’ as below but it is not addressing the real problem.
The real problem is the inappropriate intake of low-quality, calorie dense foods, lack of exercise, inadequate rest, and elevated stress.
The best diet is a ‘Hunter-Gatherer’ diet composed of lean meats, fruits, and vegetables and limiting sources of carbohydrates.
We cannot be healthy without addressing these issues!
_________________________________________________________________________
Here are the ‘Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (TLCs)’ for your information. They are not a bad idea but I do not believe that implementing the TLCs alone is going to improve your health and decrease your cardiovascular disease risks.
TLC Diet
Weight Management – the goal is to get a Body Mass Index (BMI) of less than 25
Increased physical activity: all exercise and activity is good. However, the ‘magic number’ that has been studied is 17 miles per week of running, jogging, or walking. Ideally, you will want to get at least 20-30 minutes of aerobic exercise on most, if not all, days of the week.
I have never seen anyone, not a single patient, not decrease their risk of cardiovascular disease when they optimally addressed their health through the ‘Healthy Trinity’. On the other hand, nobody decreases their risks by not doing anything.
For those that are not convinced, or too lazy, medications may be an option. At the same time, keep in mind that I believe that all medications are controlled poisons! They all have side effects. Additionally, many of these medications have not been proven to be beneficial.
With all of that being said, here is the information on medications for cholesterol
There are currently 4 classes of medications for the treatment of lipids. Each class has its own set of benefits and challenges.
Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) – has one of the best track records for improving HDL (10-30% improvement), which is often hard to do. Many people have difficulty with the side effects: flushing (lasts 20-30min typically), itching, and rashes. This typically resolves after a couple of weeks. This can be minimized with taking aspirin 30-60min prior to taking the niacin. Applesauce has been a ‘miracle food’ to reduce, if not eliminate, the side effects associated with Niacin. You should start with a very low dose (100mg) and increase 100mg every 4 days until you reach around 1500mg. Revolution Niacin is a controlled release Niacin and is available in our clinic.
This can be VERY difficult to change! HDL is often genetically determined and it is hard to change it. Here are some things that can be done:
______________________________________________________________________________________
There are 5 major classes of lipoproteins. Based on size (largest to smallest) they are:
These are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85-92%), phospholipids (6-12%), cholesterol (1-3%) and proteins (1-2%). They transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other locations in the body. These lipoproteins enable lipids, fat, and cholesterol to be transported in the blood (fats don’t mix well with water).
Chylomicrons pick up dietary cholesterol & triglycerides from the intestine and transport them to the tissues. As they circulate they exchange products with HDL (HDL donates an Apolipoprotein C-II (APOC2) and an Apolipoprotein E) and become ‘mature chylomicrons’. An enzyme, lipoprotein lipase, removes the triglycerides from chylomicrons. Once the TGs have been distributed, the mature chylomicrons are called chylomicron remnants.
VLDL is assembled in the liver from TGs, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL contains Apolipoprotein B100, Apolipoprotein C-I, Apolipoprotein E, Cholesterol, Cholesteryl Esters, and TGs. VLDL takes Apolipoprotein C-II and E (in the same manner as chylomicrons). Chylomicrons and VLDL are similar but chylomicrons transport exogenous products (things ingested) and VLDL transports endogenous products (things produced in the body).
VLDL transports TGs and cholesterol to the tissues. Lipoprotein lipase is the enzyme that removes the lipids from the VLDL. Once the TGs are deposited in the tissues, the VLDL becomes…
IDL is the product of removed TGs from VLDL. IDL has lost most of its TG but it retains cholesteryl esters. It also retains ApoB100 and ApoE. The ApoE has a very high affinity for the LDL receptor. When the IDL is converted to LDL it loses its ApoE.
LDL is generally referred to as “bad cholesterol” because LDL, when elevated, increases risk of cardiovascular disease and health problems.
Each particle of LDL contains 1 molecule of Apolipoprotein B100 and has a highly-hydrophobic core consisting of polyunsaturated fatty acid known (linoleate) and about 1500 esterified cholesterol molecules.
LDL comes in multiple particle sizes. The smaller & more dense LDL, known as pattern B, are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease because they can more easily penetrate the endothelium. There is good evidence that elevations of these smaller, more dense LDL particles are more closely associated with cardiovascular disease than a standard measurement of total LDL. However, it is more expensive (and less available) to measure these particles so it is not routinely performed by most physicians.
There are several that will more accurately measure cholesterol & LDL:
We us NMR performed through Health Diagnostics Laboratory and offer it to my patients in my clinic. It is covered by Medicare and most other insurances. If you have any kind of health insurance this test will not cost you anything! The lab does not send bills to patients no matter what your insurance actually pays. Not bad for such wonderful information! Additionally, this lab measures LDL directly so it is not impacted by food so you don’t have to be fasting for an accurate measurement of your lipids.
LDL is formed when VLDL particles release their TGs by the action of Lipoprotein Lipase. LDL particles increase the risk for cardiovascular disease as they invade the arterial endothelium & get oxidized. A complex set of biochemical reactions, stimulated by necrotic cell debris & free radicals in the endothelium, regulates the oxidation of LDL particles.
The liver is able to synthesize cholesterol via the Mevalonic Acid Pathway. The rate limiting step in this pathway is 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG CoA Reductase). This enzyme is inhibited by the Statin medications. HMG CoA Reductase activity is increased by insulin and decreased by glucagon adding to the multiple problems of excess insulin.
LDL is not directly measured by the Standard Lipid Panel but calculated by the Friedwald equation:
A reduction of small, dense LDL particle is essential for decreasing the risk of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. The target LDL for treatment varies based on the overall risk of cardiovascular disease for the patient. The goal with any therapy is to decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Modern, western medicine uses ‘target goal’ levels because they are using medications to achieve effect. Since medicines are ‘controlled poisons’ there are side effects and risks associated with their use. We treat to a target goal simply to limit the cost of therapy and minimize risks and side effects.
These particles are referred to as high-density due to the amount of cholesterol relative to protein. HDL particles contain Apolipoprotein A1 and A2. HDL transports cholesterol from other lipoproteins and tissues back to the liver and to ‘steroidogenic organs’. The steroidogenic organs need cholesterol for the production of steroids and other hormones. The process of HDL picking up cholesterol from the tissues and taking it back to the liver is termed Reverse Cholesterol Transport (RCT).
HDL helps prevent cardiovascular disease due to its ability to pick-up cholesterol and inhibit inflammation, oxidation, activation of the endothelium, coagulation, and platelet aggregation. These factors contribute to the protective effects of HDL and why low HDL levels increase risk of CVD. In fact, you decrease your risk of death 6% & cardiovascular events 3% for every 1 mg/dl you increase your HDL.
References:

The BMI is NOT a direct measurement of body composition or body fat.
The BMI is how we categorize people’s health risk based on their body weight as they (the medical research) have been able to correlate some diseases with the BMI. According to the ‘experts’ the higher the BMI the higher the risk. The BMI categories are based on the relationship between weight, disease, & death.
The BMI recommended by the medical community as a tool to help determine health risk. It is true that excess body fat decreases health but the BMI does NOT correlate with body fat.
Dr Robert Huizinga, the Medical Director for NBC’s hit show ‘The Biggest Loser”, calls the BMI the Bogus Medical Index and for good reason!
I had the opportunity to work with Dr Huizinga for several days and it was quite enlightening! During his presentations he presented 3 patients and showed pictures.
He would then ask which patient was the healthiest and which one was the ‘fattest’. Interestingly, they all had the same percent body fat at around 33%! The first patient with a BMI of 18 had what is called Sarcopenia (very low muscle mass) and was extremely unhealthy! Clearly, the BMI is not an accurate tool for this patient.
Next, he presented a male patient who was 25 yrs old, 6’1″, and weighed 270 lbs. He then mentioned that his BMI was 35 which qualified this patient for gastric bypass surgery. This patient was… Bo Jackson! Dr H described him as the fittest man he had ever had the opportunity to work with.
Any system that can confuse an extremely fit man for an obese man who needs gastric bypass is obviously flawed!
The BMI can help put patients into categories somewhat and it is certainly cheaper than performing a DEXA body composition scan on all of our patients. However, we do recommend DEXA scans for our Revolution Health & Wellness Clinic patients.
The categories are as follows:
As stated above, the higher your BMI the higher association for many medical problems such as:
The bottom line is that unless your body fat percentage is less than 15% (slightly higher for women) AND your BMI puts you in the overweight or obese category YOU NEED TO LOSE WEIGHT!
Here are some additional resources regarding weight & BMI
As an Army Doc I saw countless patients with musculoskeletal complaints.
It wasn’t uncommon that someone would come up to be asking for an MRI in order to “find out what is going on“. I often asked them if they were considering Surgey to correct the problem and the most frequent response is “no way, I just want to know what is going on!”
My residency training taught me that an MRI was a great tool to help evaluate the need for surgery and identify a surgically correctable cause for the problem. MRIs can cost over $2000 so they aren’t cheap. Somebody has to pay for it and there should be a good reason to ask for one!
A lot of tests (labs, xrays, CT, and MRI) are like picking your nose in public… what are you going to do with the results?
If an MRI is going to change my management then it is something to consider and may be worth the cost.
However, MRIs are not perfect tests!
I read an article the other day on incidental findings of meniscal damage during knee MRIs. This study evaluated the incidence of meniscal damage in patients who had no knee complaints. They evaluated 991 patients in Framingham, MA without regard to whether or not they had knee complaints and then evaluated whether or not they had any symptoms. They noted that 61% of patients with meniscal tears on MRI didn’t have any knee pain, aching, or stiffness within the previous month.
I like this study because it relays what I’ve been thinking for years…
I’ve had numerous patients tell me that they have a herniated disk and they think that is the cause of their back pain. However, on physical examination, I can reproduce their pain by palpation (by pushing on their back). I can also, almost always, dramatically reduce their pain (and in some cases make them pain free) with a prolotherapy injection that doesn’t go anywhere near their intervertebral disk!
Multiple studies have shown that there is no relationship between presence of disk herniation and symptoms.
One study (Boos et al.) evaluated patients with jobs that had high-risk of causing disk herniation (frequent bending, twisting, lifting, vibration, etc). All 96 of these patients were asymptomatic. However, the following ‘abnormalities’ were found:
And none of these patients had ANY symptoms!
If you are middle-aged (average age of 45) and you have an MRI on your lower back, here are the chances you’d have something “abnormal” on your MRI – regardless of symptoms:
So, MRIs are a valuable and useful tool. BUT we need to exercise discretion when ordering them. It is a rare instance that I need to get an MRI before prolotherapy treatments. I just haven’t found them that helpful.
References:
The problem is that Niacin, in therapeutic doses, can have some very unpleasant side effects. It can affect the liver and you should have your liver enzymes monitored while you are taking high doses of Niacin. However, the most common problem with Niacin consumption is facial flushing.
First, don’t bother taking the ‘Non-Flushing’ form of Niacin (inositol hexaniacinate). It doesn’t appear to have any benefit for lowering your cholesterol. For benefit, we need the Nicotinic Acid form of Niacin.
Niacin causes vasodilation (dilating the blood vessels) in the skin through the release of prostaglandins (PGD2) and not due to histamine. It takes time to replace this PGD2 once it is released. Therefore, if we deplete the PGD2 through Niacin and maintain the Niacin then the flushing should go away. If you stop the Niacin it will allow the PGD2 to replenish and the flushing would return the next time you take it again.
It is important to understand what you can expect with the flushing. The flushing is a skin redness, itching, and burning sensation and typically lasts 15-30 minutes then resolves spontaneously. The severity of the flushing varies from patient to patient and some patients are extremely alarmed and concerned. We have had patients tell us that they thought they were going to die.
Many times patients are relieved to know that this is not an indication of any problems in any way. We do our best to make sure that patients understand the side effects they may encounter.
The best thing is to prevent this flushing to begin with! Therapeutic doses of Niacin are often from 1.5-2 grams per day (4 tablets at 500mg each) but we recommend starting with lower doses and gradually increasing them. This gradually depletes the prostaglandins that cause the flushing and may prevent the flushing altogether.
The next thing is to take a Niacin-SR, a sustained-release niacin as lower levels of niacin are released slowly over several hours and it dramatically reduces the chances that a flush will occur as well as the severity if it does occur. This is the same principle as stated above.
Some sources recommend taking 325mg of aspirin 30 minutes before taking your aspiring. We have heard several patients state that taking Niacin with apple sauce dramatically improves the flushing.
Niacin causes flushing in some people. If you take Niacin and don’t get flushing then there is no need to make any adjustments. However, if you DO get flushing then here are some options to prevent that flushing.
You can have flushing with niacin. While it may be unpleasant and uncomfortable, medically speaking, it is not problematic. It does not suggest any problems. It is nothing to worry about. This effect typically reduces as you continue your Niacin therapy. Get your liver checked to make sure everything stays okay.
Niaspan (500mg) costs around $100 for a 30 day supply – this is the prescription version. Niacin-SR is less than $10 for the same amount.
Plantar fasciitis can be very debilitating and extremely difficult to eliminate. I’ve had it twice myself and struggled for quite some time with fixing it! The first time I had it I was able to get rid of it with constant stretching and activity modification (rest). The 2nd time stretching didn’t fix it but a night splint over several months did the trick.

Unfortunately, it is all to frequent that nothing else helps and these patients are seeking surgery as an option to finally eliminate their pain!
We have found that nearly all of our patients respond to Prolotherapy (or PRP depending on the patient) for plantar fasciitis. The procedure we use works extremely well.
While we certainly treat the source of the pain (the junction of the plantar fascia with the calcaneous), we also want to help restore the normal arch of the foot which reduces the strain on the plantar fascia. When we do that we dramatically reduce the likelihood of recurrence of plantar fasciitis.
Check out this video on Prolotherapy for plantar fasciitis and see how simple it really is! Most patients require 3-6 procedures. The healing is a process over time but it works for most patients.
Low back pain is extremely common and can be very debilitating. We have seen patients do anything under the sun to try to get relief including getting addicted to pain medications, having surgery, getting steroid injections, getting epidural injections, getting nerve blocks, etc.
It is striking how many of these patients continue to have low back pain despite all of these therapies and despite all of the costs associated with these procedures!
There are numerous problems with the way these procedures work and there are several reasons why patients still have pain. Ultimately, we have to find the ultimate source of the problem for their low back pain and fix that.
When we know what we are dealing with we are far better equipped at being able to fix the problem.
We have found that most people have low back pain because of ligament or tendon laxity or weakness. Sure, herniated disks occur but we believe that the vast majority of them occur because the facet joints are weakened and put excess strain on the disks. Additionally, numerous patients have herniated disks but don’t have any pain. Interesting!
Prolotherapy & PRP address the ligament or tendon laxity or weakness and returns it to normal function and strength which eliminates the pain. Steroid injections don’t do this. Surgery doesn’t do this. Nerve blocks don’t do this. This is why they often fail.
This video is the Prolotherapy procedure but PRP is essentially the same process, it just uses your processed blood (platelets) as the solution. This patient had no anesthesia, sedation, or pain medications before or during the procedure (except the lidocaine in the solution) and she tolerated it extremely well.
Warning: do not watch this video if you are squeamish about needles!
Contact us today so that we can help you eliminate your back pain today!
Prolotherapy is an excellent therapy that stimulates that body to heal the painful, damaged areas.
Prolotherapy stimulates the repair of injured, damaged structures. It involves the injection of a proliferant solution, which is all natural, (along with anesthetics to decrease the pain associated with the injections) at the exact site of an injury (ligaments, tendons, menisci, muscles, growth plates, joint capsule, and cartilage) so that the immune system is stimulated to repair the damaged area. Inflammation is the process by which the body heals itself.
Specifically, Prolotherapy causes proliferation of fibroblasts (where the term Prolotherapy comes from). Fibroblasts are the cells that produce the collagen which grows the ligaments and tendons. Fibroblast proliferation stimulates new, strong, collagen tissue which is what is needed to repair ligament/tendon sprains and other sports injuries.
ISN’T THE PAIN AN INDICATION OF TOO MUCH INFLAMMATION?
The body heals through an inflammatory reaction. The inflammation is what heals the damage to the ligaments & tendons which is caused by sports injury or trauma. Persistent pain in the athlete indicates that these tissues are still damaged. Persistent pain is not normal and should let the athlete know that there is persistent damage to these structures. The appropriate response for the athlete should be to obtain prolotherapy as opposed to the common response of taking anti-inflammatory medications. These medications have been shown to reduce the healing and cause further weakening of the damaged structures.
IF ANTI-INFLAMMATORIES AND CORTISONE WEAKEN TISSUE THEN WHY DOES THE PAIN GO AWAY?
The best way to explain this is to compare it to the check engine light in your car. When the light comes on it indicates a problem. You have 3 options when the light comes on:
WHY DO DOCTORS RECOMMEND THESE MEDICATIONS IF I NEED THIS INFLAMMATION?
The principle of optimal healing is not ‘standard medicine.’ When I was an Athletic Trainer in collage, we had shirts that said “Just Ice It.” RICE is the treatment for nearly all musculoskeletal problems.
This is similar to the mercury toxicity issue. It is clear from the government standpoint that mercury is toxic to the human body as there are strict guidelines for mercuries use in industry and industry exposure. The Environmental Protection Agency has clear guidelines to how much exposure of mercury is ‘safe’ in the workplace and the environment, yet the government allowed and still allows dentists to put mercury directly into the mouths of Americans via amalgam fillings. For the American Dental Association and other ‘authoritative’ agencies to now ‘admit’ that mercury is a poison (which it clearly is) could cause anarchy and tremendous legal action.
You can imagine that there would be a huge backlash if the medical community suddenly reversed their position. What if they admitted that NSAIDs and steroids actually inhibited the healing process and were the primary cause of arthritis. Can you see the commercials from the lawyers?
Athletes should not tolerate the medical therapy! Please help us let every athlete know how to restore their ligaments/tendons and keep them in the game longer! Tell everyone you know about the benefits of Prolotherapy & PRP!
There are some potential complications that can be encountered with the procedure and it is very important that every patient understands these potential risks. We recommend that each patient watch the video below to gain a greater understanding of the potential risks. Each patient will be given an opportunity to ask questions about these risks in relation to their specific procedure.
The majority of the risks associated with Prolotherapy & PRP are inherent with the needle injection. These risks include:
As stated in the video, this is an injection technique where we are injecting an irritating solution into already painful areas. So, yes, it can be painful. Most of our patients tolerate the procedure very well but some do have extreme pain during the procedure.
We are committed to keeping you as comfortable as possible during the procedure as well as afterwards. There are several things we can do to help reduce the discomfort of the procedure.
Medications: there are several medications that can be prescribed and taken prior to the procedure to help you stay as comfortable as possible. Here is a short list of medications that we can use. If any of these medications are prescribed for you then you will need to take them exactly as they are prescribed.
You may be prescribed all, some, or none of these medications. If you take any of these medications prior to your procedure then you will need to have a driver to bring you to the clinic and back home.
Topical anesthetic: we can apply a topical anesthetic that will numb the skin so that the pinch of the needles is reduced. This does not help with the deeper pain or discomfort. This anesthetic takes between 45-60 minutes for full effect so you will need to let us know that you want this and arrive 1 hour prior to your procedure.
Tennant Biomodulator: this is a specific device similar to a TENS unit (but different in effect) that can help distract from the procedure. Some patients get significant benefit from this device. This is easy to do in the clinic. We simply attach the electrodes to certain areas, turn on the device, and increase the intensity as high as you can tolerate. The more you can tolerate the more benefit you will receive.
Sooting music, Squeeze balls: The more relaxed you are the more comfortable you will be. The squeeze balls seem to help a little as well.
IV Medications: we can do some light sedation by giving you pain medications and anxiety medications through an IV. These medications kick-in within minutes and can make you extremely comfortable. We do not completely sedate you. We want you awake and able to interact with us during the procedure. However, these medications may induce amnesia so you may not remember have the procedure performed once the medications wear off.
It will take several hours to return to ‘normal’ after having these medications and the procedure only takes minutes so we have to decide if it is worth it. There is an additional fee associated with IV medications due to the level of supervision required, IV supplies, medications, etc. It takes a significant amount of resources to make sure that this can be done safely!
Our goal is to resolve your pain as quickly, cost-effectively, and comfortably as possible.
We are Tulsa’s premiere functional medicine clinic combining an ideal blend of traditional medicine with holistic & natural medicine. We believe that sleep is critical for optimal health and must be considered as part of a holistic approach to optimizing each patient’s health.
The US Army has a number of ‘schools’ that are designed to train soldiers for combat or certain skills. Some of these courses must induce certain levels of stress. The number one, most-effective way of inducing stress is sleep deprivation.
The absence of sleep or insufficiency of sleep causes a number of problems. It has been suggested that Fibromyalgia has its roots in a lack of sleep. In fact, one study was able to induce symptoms of fibromyalgia after disrupting sleep for just 7 days!
Lack of sleep increases stress and fatigue. It increases cortisol levels which disrupts blood sugar control and increases insulin resistance.
Lack of sleep can derail weight loss, increase illness, inhibit muscular growth, and make just about everything worse!
So what do we do about it?
Well, like every other medical problem, we need to determine the CAUSE of the problem. Insomnia is not THE problem, it is a symptom of the REAL problem.
This is a simple survey that you can take to measure your general level of sleepiness. A total score of 10 or more suggests the need for further evaluation. It is important for your doctor to identify if you have an underlying sleep disorder.
Here is a pretty good article on sleep and what you can do about it.
Insomnia & sleep disturbance is treatable! Long-term, the best solution is addressing the steps above to treat the problems that are causing the insomnia. However, some patients are having such difficulty that they need some immediate intervention.
My first recommendation for a supplement that can help with sleep is Revolution.calm. This is a fantastic product, all natural, and give excellent results. Some patients notice significant benefits immediately while others notice an improved sleep over about a month or so. We generally recommend starting with 1 scoop mixed in water twice daily. You can increase or decrease your dose until you find the perfect amount for you and your needs. This is not a ‘sleep aid’ per se. It is a neuro-endocrine stabilizer meaning that it improves the function of your brain and endocrine systems. When these system are improved your sleep improves.
Natural Sleep Aids: the two with the best evidence supporting them are Melatonin & Valerian. Both of these are safe and can be very effective. Valerian seems to be effective for up to 4-6 weeks and then you may need a break from it. Melatonin is produced by the pineal gland within our brain and helps with our circadian rhythm. It can help ‘reset the clock’ so to speak to improve sleep.
Medications: there are several classes of medications that can be used (primarily short-term use) to help get started with sleep improvement. We generally do not recommend these medications as there are significant side effects and potential problems with each of them. Consider these medications with extreme cautions.